Cultivating Mind-Body Wellness: Innovative Approaches to Nervous System Regulation
Do you want to discover how to control your nervous system and improve your mental and physical health? You're in the right place! Dive into the world of nervous system regulation with us!
Our nervous system is like a command center, steering everything from how we move to how we feel. We can also enhance our mental and physical well-being by exploring how it works and how to tune it.
From simple breathing exercises to mindful movement, eating right, and staying hydrated, there are many paths to support our nervous system. These steps can help us find more balance, energy, and joy daily.
Let's embark on this journey to understand and harness the power of our nervous system for a healthier, happier life!
Deepening the Understanding of the Nervous System and Its Regulation
The nervous system, an intricate and expansive network of neurons and supporting cells is fundamental in transmitting signals within the body, thereby orchestrating a symphony of bodily functions and responses.
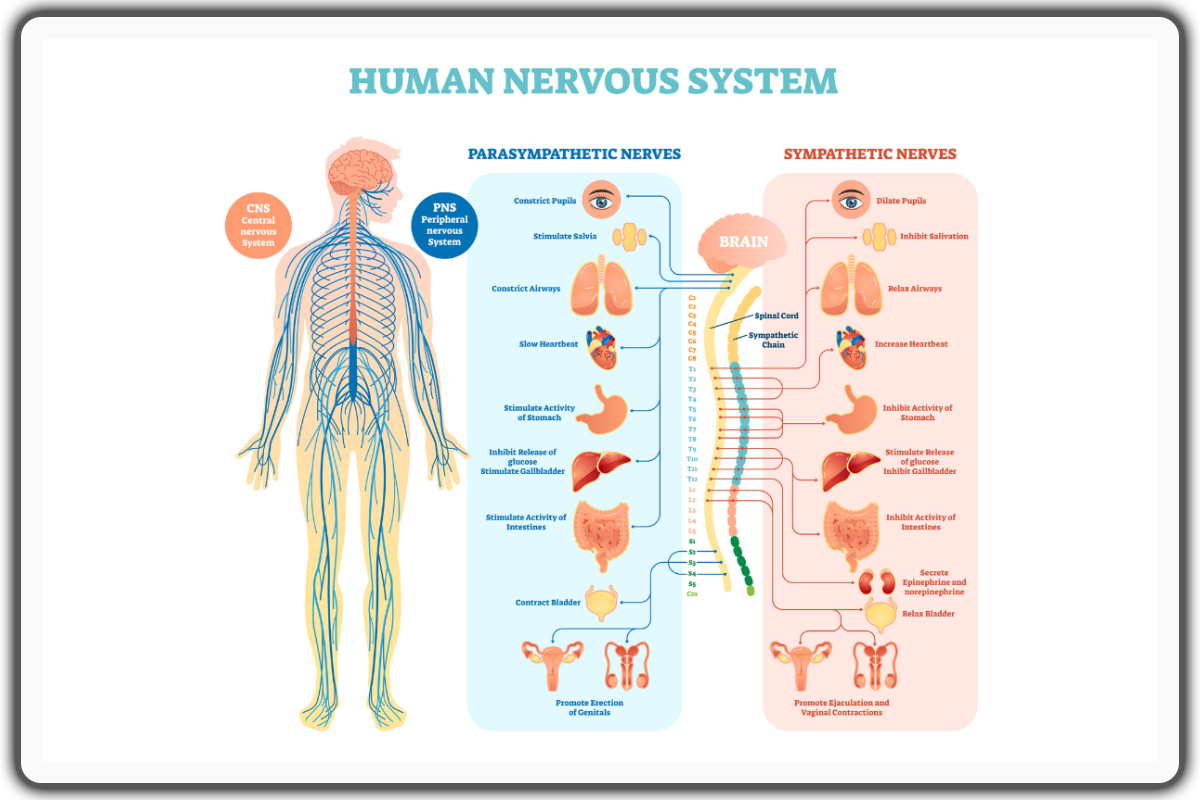
It is divided into two primary components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Central Nervous System (CNS)

The CNS, encompassing the brain and spinal cord, serves as the control center for the body. It processes sensory information and facilitates cognitive functions, emotions, and memory.
The brain, in tandem with the spinal cord, directs bodily functions, illustrating the critical role of the CNS in overall health and well-being.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The PNS extends beyond the CNS, consisting of nerves that transmit information among the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body. It includes the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which is further subdivided into the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system.
These subsystems govern essential bodily functions beyond conscious control. The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for responses associated with 'fight or flight,' whereas the parasympathetic nervous system facilitates functions related to 'rest and digest.'
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) and Health
The ANS maintains homeostasis by regulating vital functions such as blood pressure and heart rate. Imbalances in this system, often triggered by chronic stress, can lead to dysregulated nervous system functions, impacting both physical and mental health.
Furthermore, this mini-review article of Christensen et.al (2020) [²], published in Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, discusses the role of the ANS in sensory modulation, emphasizing the complex interactions between the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
It highlights how patterns of ANS activation vary across individuals and influence automatic behavioral responses.
The study emphasizes the importance of understanding stress patterns within the ANS for effective treatment of children with sensory modulation disorder.
Nervous System Dysregulation and Its Impacts
Dysregulated nervous system functions, particularly chronic stress, can exacerbate or trigger a range of health issues. When released excessively, stress hormones can disrupt the delicate balance of the nervous system, leading to adverse effects on physical health, including elevated blood pressure and impaired immune function.
The nervous system's vast and dynamic nature underscores its significance in regulating mental and physical health. By employing nervous system regulation techniques, such as deep breathing, individuals can influence their autonomic nervous system, enhancing their resilience to stress and promoting overall well-being.
Furthermore, understanding the roles and functions of the CNS, PNS, and their respective components is crucial for grasping the full spectrum of the nervous system's influence on health and disease, highlighting the intertwined nature of mental and physical health.
Importance of Nervous System Regulation
Regulating the nervous system is crucial for maintaining overall health. The nervous system, encompassing the central and peripheral systems, controls bodily functions like heartbeat, breathing, and digestion. It's also key for mental and physical well-being.
The autonomic nervous system, comprising the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions, plays a vital role in regulating the body's stress response and promoting relaxation. Proper nervous system function ensures balanced physical responses and mental states, reducing the impact of stress and also enhancing resilience.
Moreover, techniques like deep breathing can activate the vagus nerve, promoting calm and countering stress effects. Research indicates that managing nervous system activity can improve health outcomes, emphasizing the connection between a well-regulated nervous system and improved physical and mental health.
For instance, a study in the "Journal of Clinical Neuroscience" [³] highlights the vagus nerve's role in parasympathetic control and its health implications.
Thus, understanding and regulating the nervous system is essential for optimal health and well-being.
Factors That Impact Nervous System Regulation
The regulation of the nervous system is influenced by various factors that can affect its function and efficiency.
Here are some key factors that impact nervous system regulation:
1. Stress: Chronic stress can lead to dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, increasing the production of stress hormones and affecting both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system functions.
In a study of Teixeira et al. (2015), published in PLOS ONE [¹], discusses that chronic psychological stress, which increases a stress hormone called cortisol, can make it harder for people in business roles to think clearly and perform well, no matter if they are male or female.
In men who have been stressed for a long time, their body's automatic stress response system doesn't react as strongly as it should when faced with a new stressful situation.
2. Diet: Nutritional intake is crucial to nervous system health. Deficiencies in certain nutrients, like B vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids, and magnesium, can affect neural function and regulation.
3. Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for the nervous system to repair and regenerate. Insufficient sleep can result in diminished cognitive abilities and disrupted stress response.
4. Exercise: Consistent physical activity can boost the nervous system's effectiveness, refining its response to stress and promoting balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches.
5. Mental Health: Mental states such as anxiety and depression have the potential to impact the regulation of the nervous system, affecting how the body responds to stress.
6. Substance Use: Alcohol, drugs, and even caffeine can impact the nervous system's regulation, altering mood, cognition, and stress response.
7. Social Connections: Positive social interactions can enhance vagus nerve activity, promoting a more regulated and resilient nervous system.
8. Environment: Environmental factors, including toxins or chronic noise exposure, can disrupt nervous system function and regulation.
9. Genetics: Genetic predispositions can influence the nervous system's susceptibility to various external and internal factors, affecting its regulation.
10. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Participating in activities like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can positively impact the regulation of the nervous system. These activities can enhance the body's ability to relax and activate a relaxation response.
Understanding these factors can help adopt strategies to maintain or improve the regulation of the nervous system, contributing to better physical and mental health.
Techniques for Nervous System Regulation
Understanding nervous system regulation techniques is essential for managing stress and enhancing overall health.
Deep breathing stimulates the vagus nerve, a critical component of the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and stress reduction.
This illustrates the interrelation between mental and physical health and underscores the significance of sustaining a harmonious nervous system.
Techniques to Optimize Nervous System Regulation - Breathwork and Deep Relaxation
To optimize nervous system regulation, breathwork and deep relaxation are effective techniques that influence the autonomic nervous system, promoting a shift from the stress-induced sympathetic state to a calm parasympathetic state.
Breathwork involves conscious control of breathing patterns to influence mental, emotional, and physical states.
Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing, where deep breaths are taken from the belly, help reduce stress, improve focus, and stabilize mood.
Similarly, the 4-7-8 technique involves inhaling, holding, and exhaling breath at specific intervals, which can induce relaxation and improve sleep.
Deep relaxation, such as progressive muscle relaxation, guides you to tense and then relax different muscle groups, enhancing body awareness and releasing tension.
Visualization and guided imagery can transport the mind to a peaceful state, reducing cortisol levels and enhancing well-being. Integrating these practices into daily routines can enhance mental clarity, emotional stability, and overall physical health, fostering a well-regulated nervous system.
Techniques to Optimize Nervous System Regulation - Movement and Exercise
1. Breaths
- Lie on your back on the floor, maintaining good alignment with your head, shoulders, hips, and legs.
- Then, place your arms at your sides with your palms facing upward.
- Finally, close your eyes and take several deep belly breaths, in through your nose and out through your mouth, relaxing your entire body.

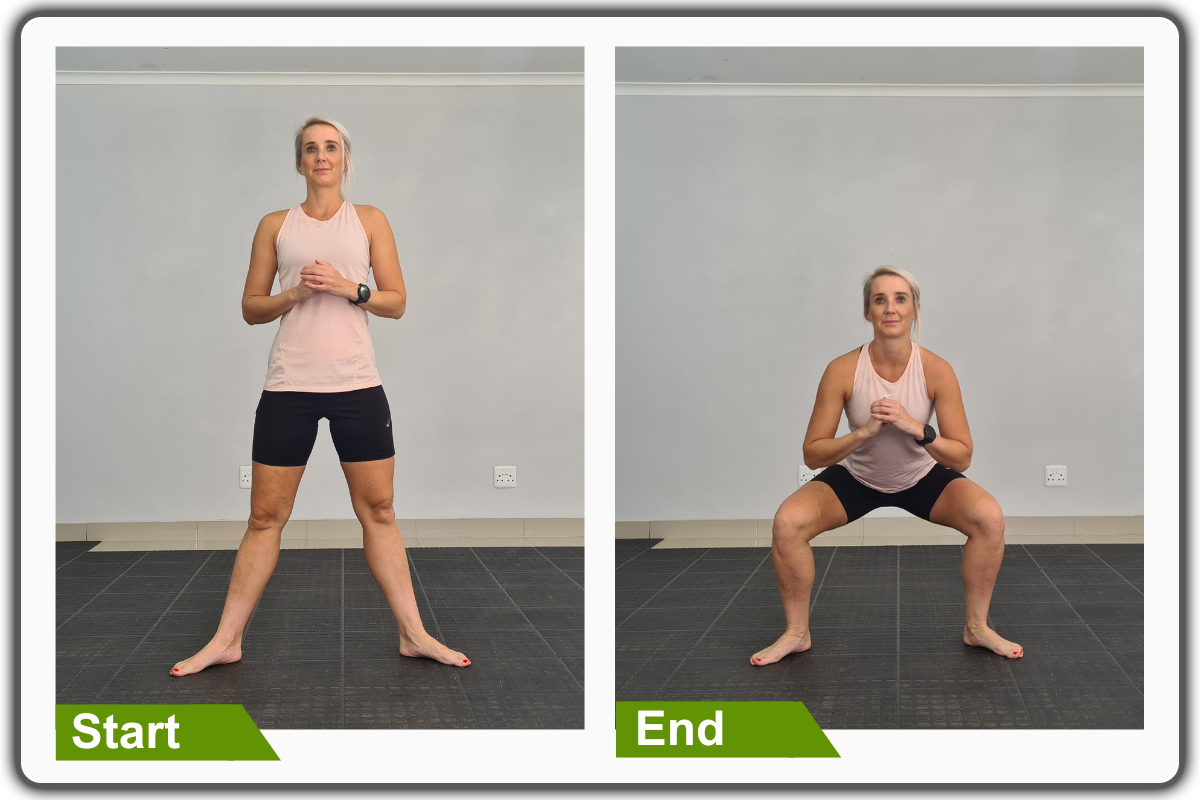
2. Squats
- Firstly, begin in an upright standing position with your feet wider than shoulder-width apart, maintaining good alignment in your upper body.
- Hold your hands together at chest height.
- Then, tighten your abdominal muscles. Bend your knees and hinge through your hips to move into a squat position.
- Keep your knees aligned with your ankles and toes.
- Press from your heels to raise back up to an upright standing position, squeezing your glutes at the top position.
- Repeat the movement.

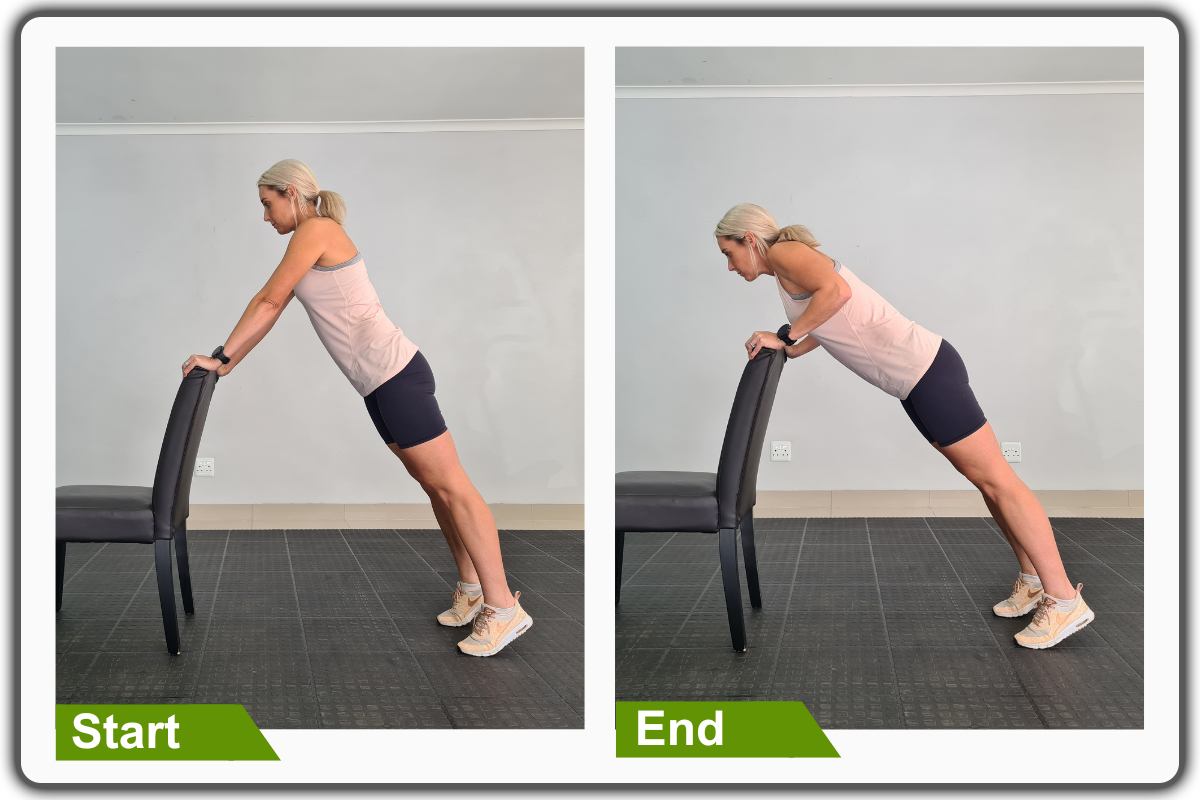
3. Push-ups
For this exercise, utilize the back of a chair or wall.
- Begin in an upright standing position with your hands against the back of a chair.
- Move your feet back to increase the angle of your body, keeping your head, shoulders, hips, and legs in good alignment.
- Engage your core.
- Then, take a deep breath, bend your arms, and lower your upper body towards the chair. Exhale and straighten your arms to complete the pushup movement.
- Lastly, perform the movement in a smooth, controlled manner, focusing on engaging your chest, arms, and core throughout the movement.

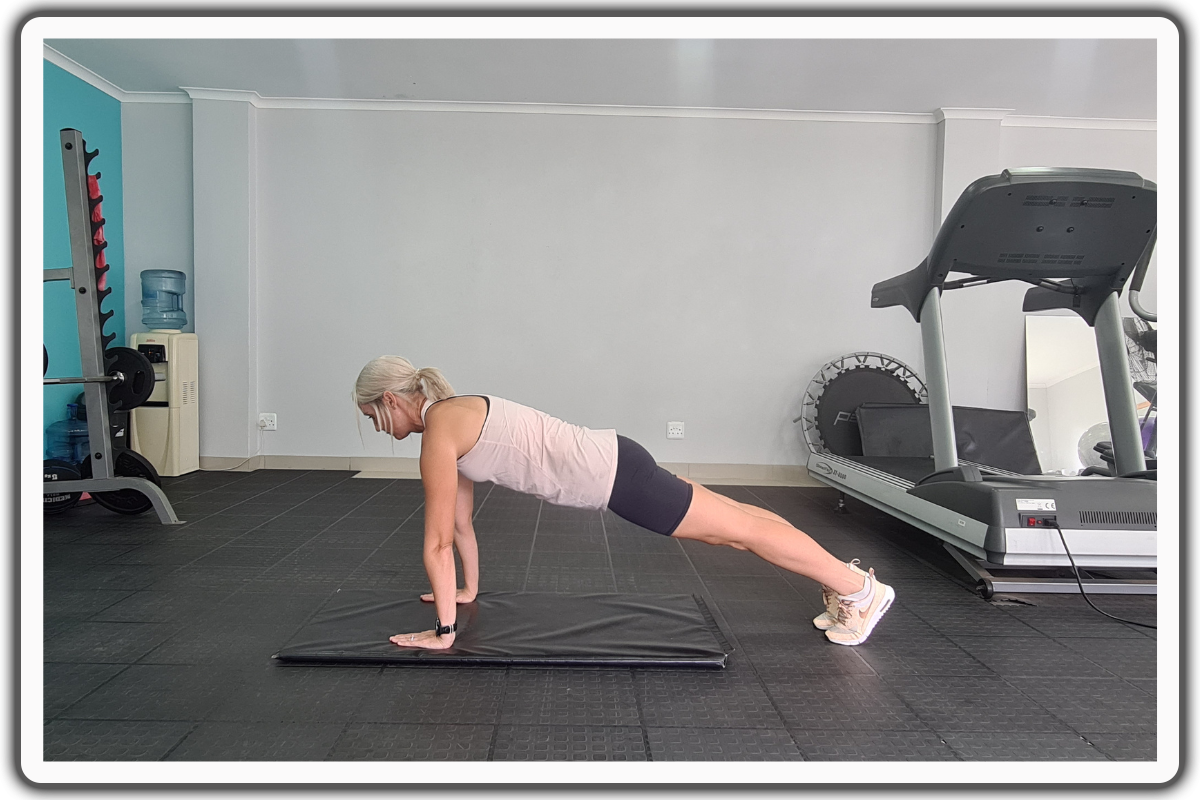
4. Full Plank
- Move into a straight-arm plank position, maintaining proper alignment with your head, shoulders, hips, and toes.
- Engage your core and then hold this position for 30 seconds to a minute, taking deep belly breaths, in through your nose and out through your mouth.
- Then, relax and return to the starting position.
- Repeat the movement as needed.

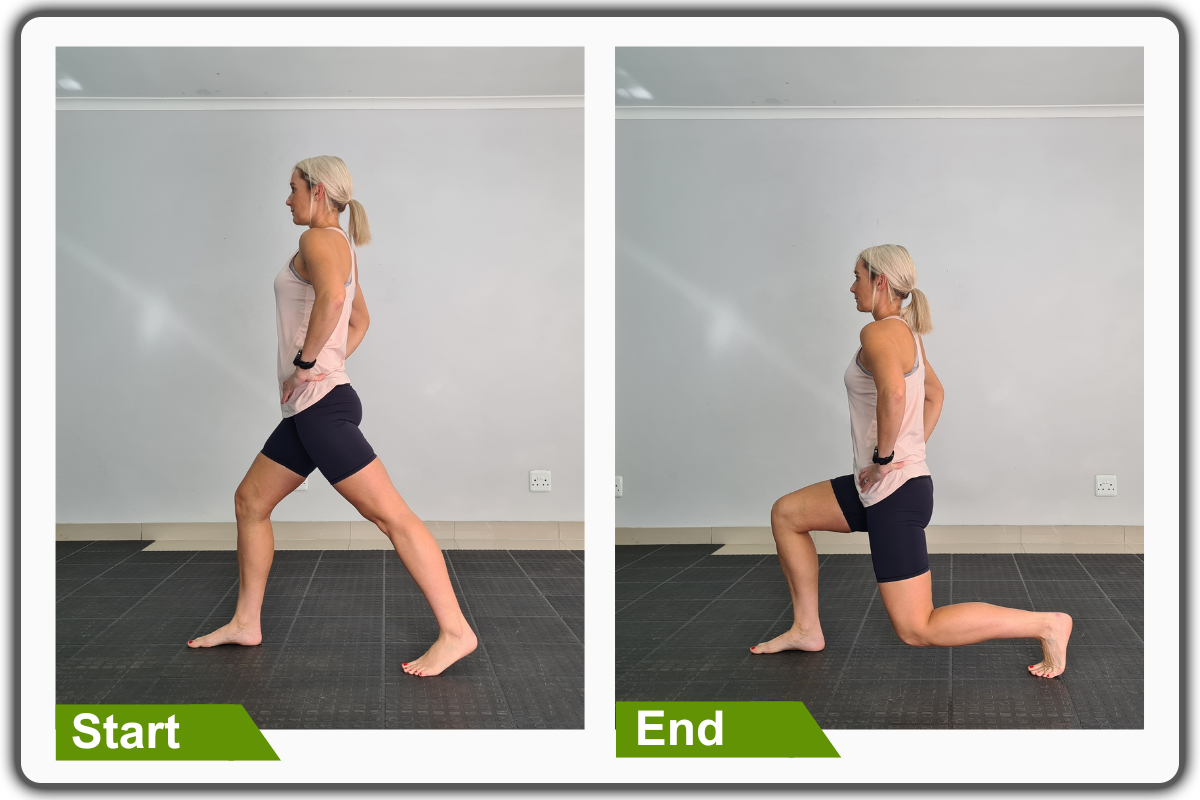
5. Lunges
- Firstly, begin in an upright standing position, maintaining good alignment with your head, shoulders, hips, and legs.
- Engage your core.
- Then, take a big step back with one foot, keeping your toes pointing straight ahead.
- Bend your front knee directly over your ankle, creating a 90-degree angle from the body, and then lower your back knee to the ground.
- Hold this position for a couple of deep belly breaths, in through your nose and out through your mouth.
- Lastly, raise back up to return to the starting position and repeat the movement on the opposite side.
- Complete for 12 repetitions on each side.

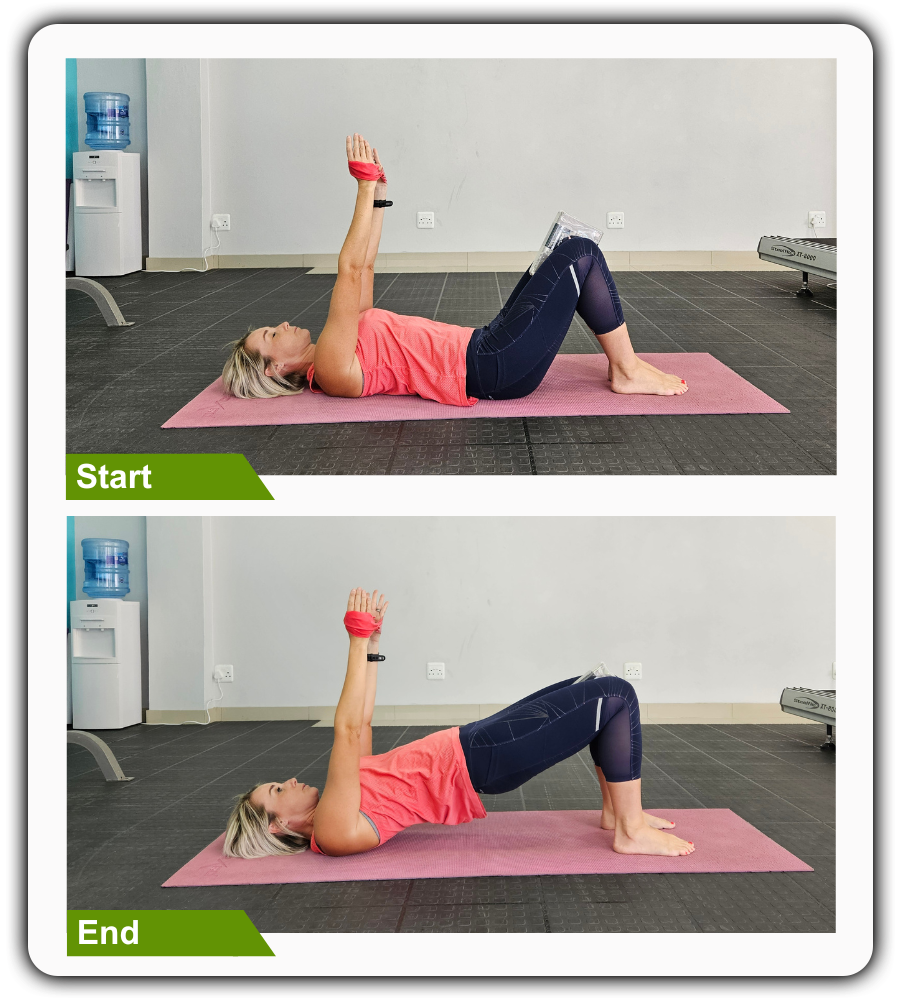
6. Glute Bridges
For this exercise, use a yoga block, bolster, or any dense object that you can squeeze between your knees.
- Lie on your back on the floor and loop the resistance band around your wrists, extending your arms toward the ceiling.
- Then, bend your knees, flatten your feet on the floor, and then squeeze the block between your knees.
- Engage your core and inner thighs, then push from your heels to lift your hips.
- Hold this position for several deep belly breaths, in through your nose and out through your mouth.
- Lastly, relax and return to the starting position.

7. Mountain Climbers
For this exercise, utilize a bench, wall, or the back of the chair for support.
- Begin in an upright standing position in front of the exercise bench with your feet shoulder-width apart, maintaining good alignment in your upper body.
- Bend forward to place both hands on top of the exercise bench, moving your feet back to increase the angle of your body.
- Contract your core, then drive one knee up towards your chest.
- Lastly, return back to the starting position and repeat movement on the opposite side.

Techniques to Optimize Nervous System Regulation - Nutrition and Hydration
Understanding nutrition and hydration's role in optimizing nervous system regulation is crucial. The nervous system governs our body's functions, and providing it with the right nutrients and adequate hydration can significantly impact its efficiency and health.
Nutrition
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts contain omega-3 fatty acids, which are vital for brain health. They also aid in maintaining cell membrane health and facilitate communication between nerve cells.
- Antioxidants: Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, nuts, and leafy greens, can shield the nervous system against harm induced by free radicals, thereby supporting its optimal function.
- B Vitamins: B6, B12, and folic acid, found in whole grains, meats, and vegetables, are crucial for nerve health and help produce neurotransmitters.
- Magnesium: This mineral, found in nuts, seeds, and leafy greens, is crucial in nerve transmission and muscle relaxation and vital for nervous system balance.
- Water: Staying well-hydrated is essential for maintaining the conductivity of nerve impulses. Lack of hydration may also result in diminished cognitive function and delayed nerve responses.
Water is integral to the nervous system's operations. It aids in maintaining electrolyte balance, which is vital for transmitting nerve impulses. Insufficient hydration can also impair cognitive function, slower response times, and inefficiency of the nervous system.
Moreover, incorporating a diet rich in these nutrients and ensuring adequate hydration can support the nervous system's functions, promoting overall physical and mental health.
This approach underscores how the nervous system plays a pivotal role in our well-being and how nutrition and hydration can enhance its regulation.
Conclusion
Want to feel and think better? Learn about your nervous system—it's like the boss of your body's activities. We've shown how it works and ways to help it do its job well.
By trying out simple things like calm breathing, moving more, eating good foods, and drinking plenty of water, you can help your nervous system.
This can also make you feel more balanced and full of life.
So, take these tips and use them every day to boost your health and happiness. It's your chance to make the most of your mind and body!
References
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnint.2020.00006/full
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7915331_Vagal_nerve_stimulation_A_review_of_its_applications_and_potential_mechanisms_that_mediate_its_clinical_effects
