Flu Fighters: Essential Prevention Tips for Everyone
Disclaimer: Please keep in mind that the content provided is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical guidance. Before trying out any of these methods, it is important to remember that some methods may work for one person, while for others, they won’t. It is highly suggested that you ask a medical professional for a personalized method that works for you.
Each one of us plays a crucial part in the battle against the flu.
Taking simple yet proactive steps can help shield ourselves and those around us from Influenza’s influence.
This article can serve as your personal flu prevention guide, offering practical strategies for staying healthy and resilient.
With the power of knowledge and action, we can stop the spread of the flu while ensuring the safety of our well-being and that of others.
Keep reading as we discuss the flu, how it spreads, its symptoms, and what we can do to prevent it from infecting us.
What is the Flu?
Influenza, commonly known by everyone as the flu, is an infectious respiratory disease triggered by influenza viruses.
It can range from mild to severe, sometimes leading to serious complications.
There are three types of flu viruses: Type A, Type B, and Type C.
You might be wondering, what about the more severe ones like the H1N1 Virus or the Bird Flu?
Those are severe variations of the Type A flu virus that rarely affects humans.
The seasonal flu in the country, which affects approximately 20% of the population, is caused by both the Type A and B viruses (Greenbaum & Meinett, 2009).
While the Type C flu virus also causes flu it is much less severe compared to A & B.
All three types of flu spread mainly through respiratory droplets when infected people cough, sneeze, or talk.
It can also spread when individuals touch surfaces or objects contaminated with the virus and subsequently touch their mouth, nose, or eyes, creating a pathway for the virus to enter the body.
The flu is especially common in young children, older adults, and people with certain underlying health conditions.
Those infected with the flu can be identified with the following symptoms:
- Fever - Fever is a common flu symptom and is often one of the first signs. It can range from mild to high-temp fevers.
Coughing - A persistent dry or sometimes productive cough is the key sign of the flu. It can be quite bothersome and may worsen over time.
Sore throat - Many people with the flu experience a sore throat, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain, especially when swallowing.
Runny or Stuffy Nose - Nasal congestion, accompanied by a runny or stuffy nose, is another common flu symptom. This can contribute to difficulty breathing through the nose.
Body Aches - Body aches, often described as muscle or joint pain, are typical flu symptoms. They can be widespread and severe, making movement uncomfortable.
Fatigue - Fatigue is a common flu symptom and can be debilitating. It often accompanies other symptoms and can significantly impact daily activities.
Vomiting - While vomiting is less common in adults with the flu, it can occur, especially in children. When present, it's usually more common in the early stages of the illness.
Diarrhea - Like vomiting, diarrhea is not as common in adults with the flu but can occur, particularly in children. It's more commonly associated with certain strains of the flu virus.
Get a flu shot or vaccine. This is the most effective way to prevent flu.
However, not everyone is keen on the idea of taking shots or vaccines.
Let's look at some other flu prevention tips that might work for you.
Vaccination
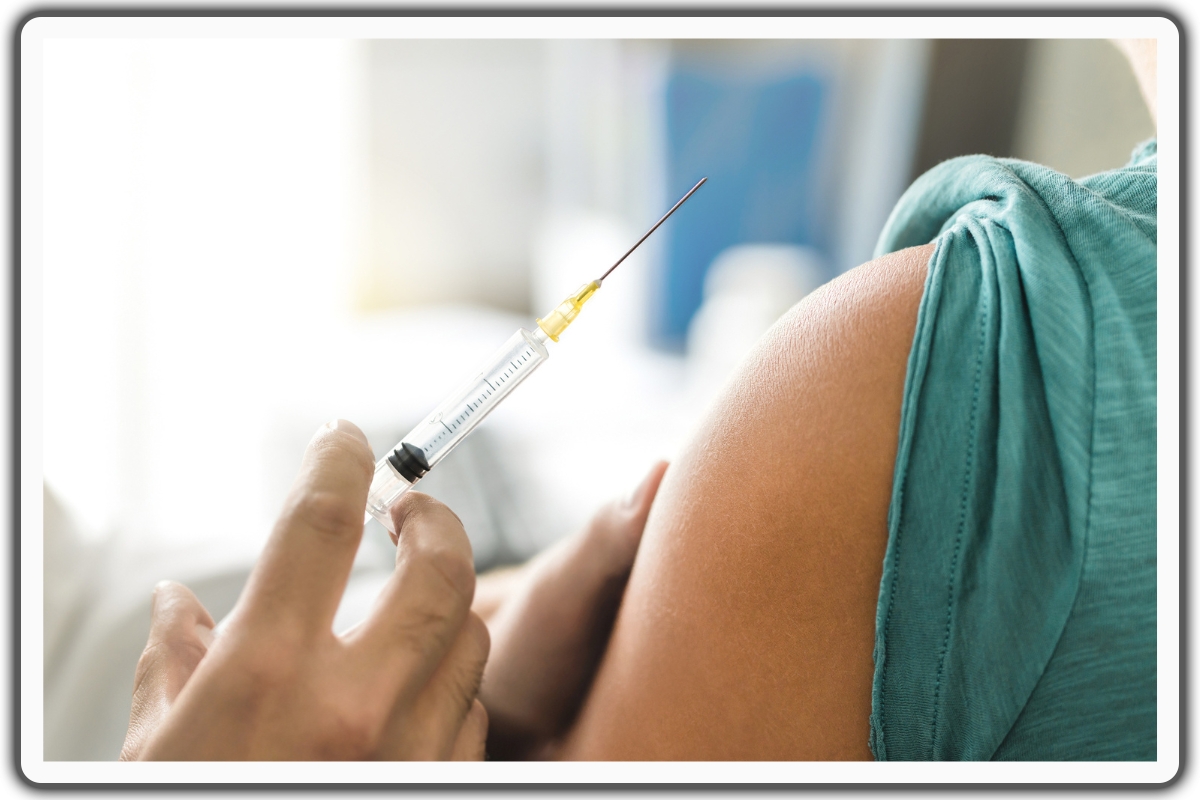
Vaccination is very important in preventing the flu.
It significantly decreases the risk of contracting the influenza virus and experiencing its symptoms.
The flu vaccine contributes to community health by creating herd immunity, making it harder for the virus to spread, and protecting the more vulnerable people (Allen, 2024).
However, common concerns such as vaccine effectiveness and safety need to be addressed.
It's essential to emphasize that flu vaccines are carefully designed to be safe and effective, with rare serious side effects.
Annual vaccination is emphasized to account for the ever-changing nature of the flu virus.
It ensures ongoing protection and bolsters personal prevention efforts against seasonal outbreaks.
Hygiene Practices
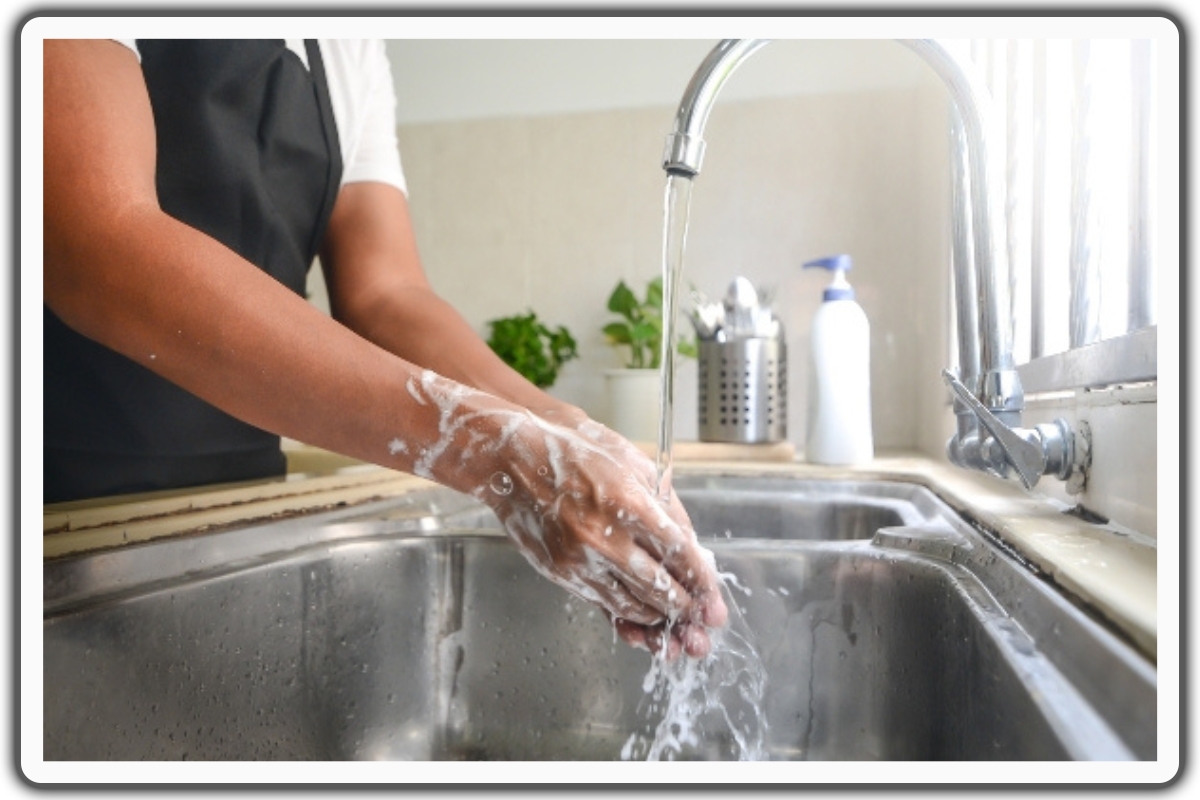

Hygiene practices are essential in preventing flu transmission.
Proper handwashing, involving thorough scrubbing with soap and water, reduces the risk of infection.
When going out, having an alcohol-based hand sanitizer for disinfecting yourself on the go is handy.
Covering the mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow also helps contain infectious droplets and minimize airborne transmission.
Most importantly, avoid close contact with sick individuals or public areas with frequently touched surfaces (American National Red Cross, 2020).
These methods reduce the risk of exposure to flu viruses, especially during flu season.
These simple yet effective practices are crucial in individual flu prevention efforts.
Cleanliness and Disinfection
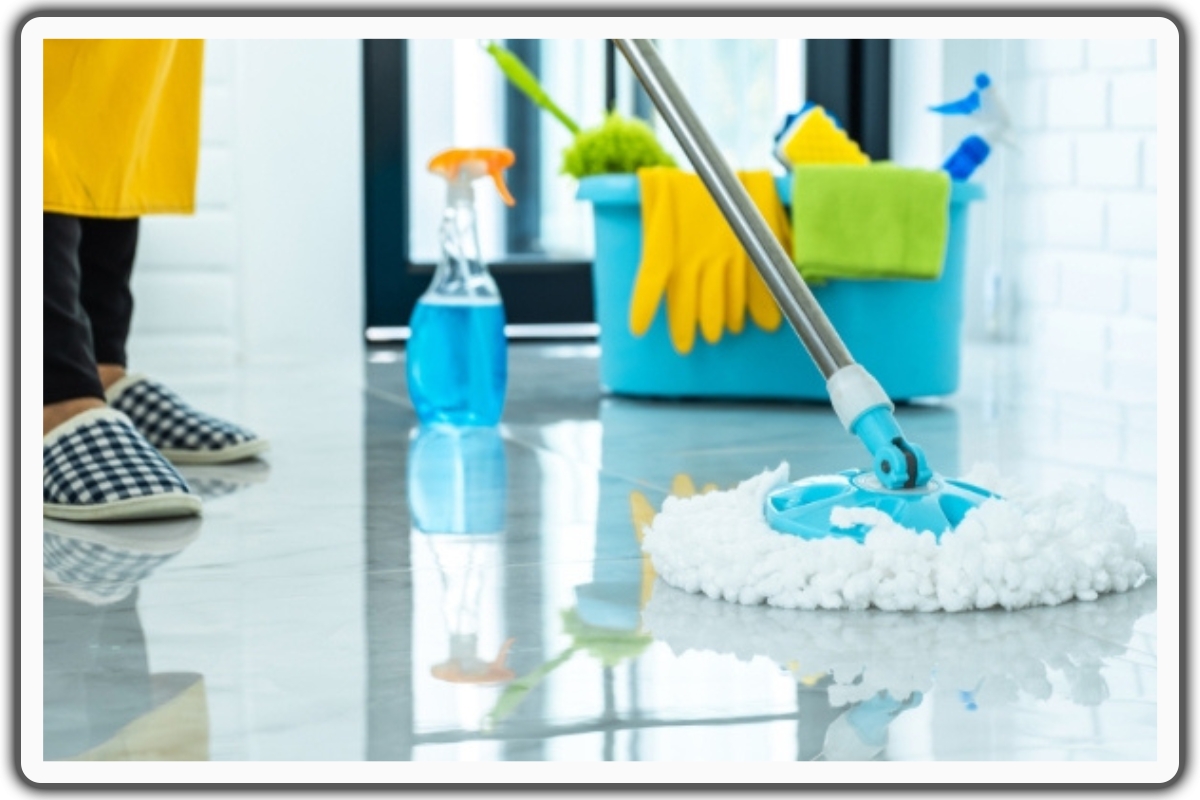

Maintaining cleanliness and disinfection practices is required for flu prevention.
Regularly cleaning and disinfecting helps remove germs and reduce the risk of contamination.
Establishing cleaning routines, using effective disinfectants, and ensuring proper ventilation contribute to a healthier environment and minimize flu transmission.
Everyone plays a crucial role in flu prevention by taking responsibility for cleanliness in personal spaces.
By practicing good hygiene, we can play a crucial role in minimizing the spread of flu viruses within communities.
Lifestyle Factors
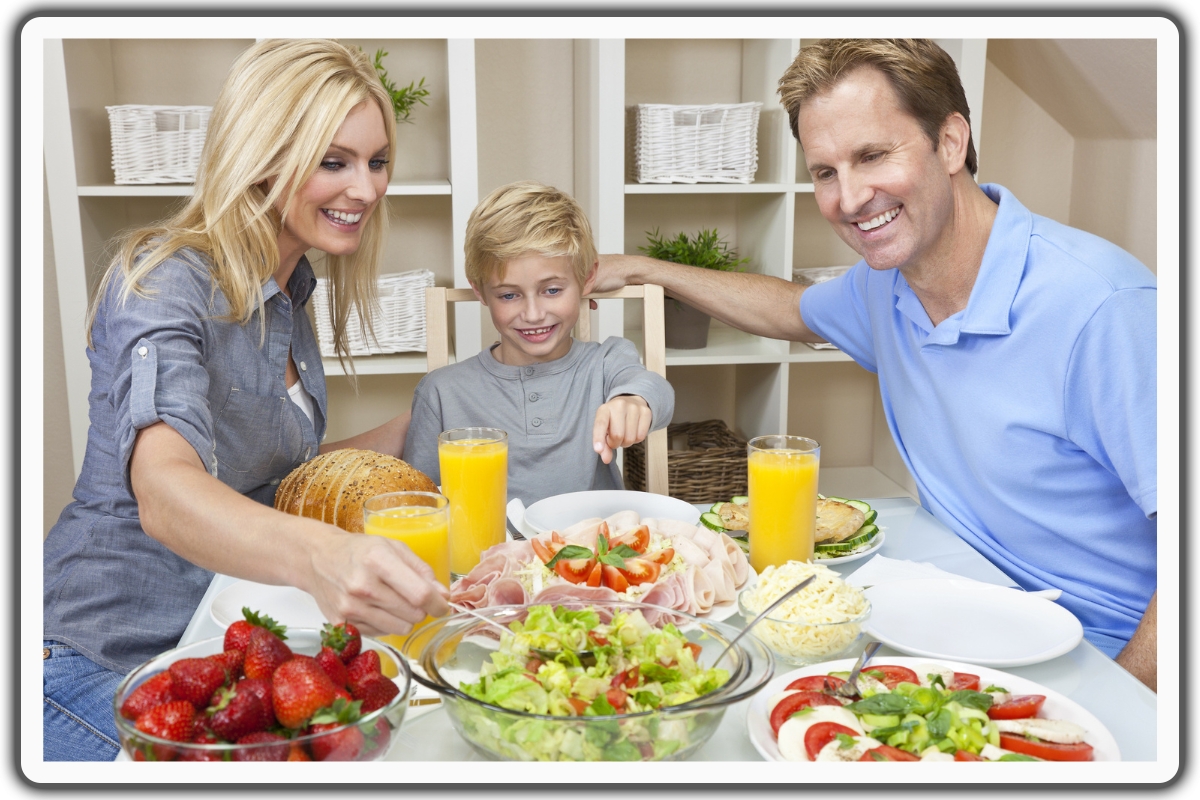

Lifestyle factors also help aid in flu prevention.
Prioritizing adequate sleep, aiming for 7-9 hours per night, supports a strong immune system that fights infections like the flu.
People need to eat nutritious food. Not only can it promote healthy eating habits, but it can also prevent flu symptoms.
By being healthy, you help strengthen your immunity and reduce susceptibility to the flu.
Regular exercise also helps, as it stimulates the immune system, increases circulation of immune cells, and reduces inflammation.
Incorporating these lifestyle factors into daily routines enhances personal immunity against the flu and supports overall health and well-being.
Stress Management
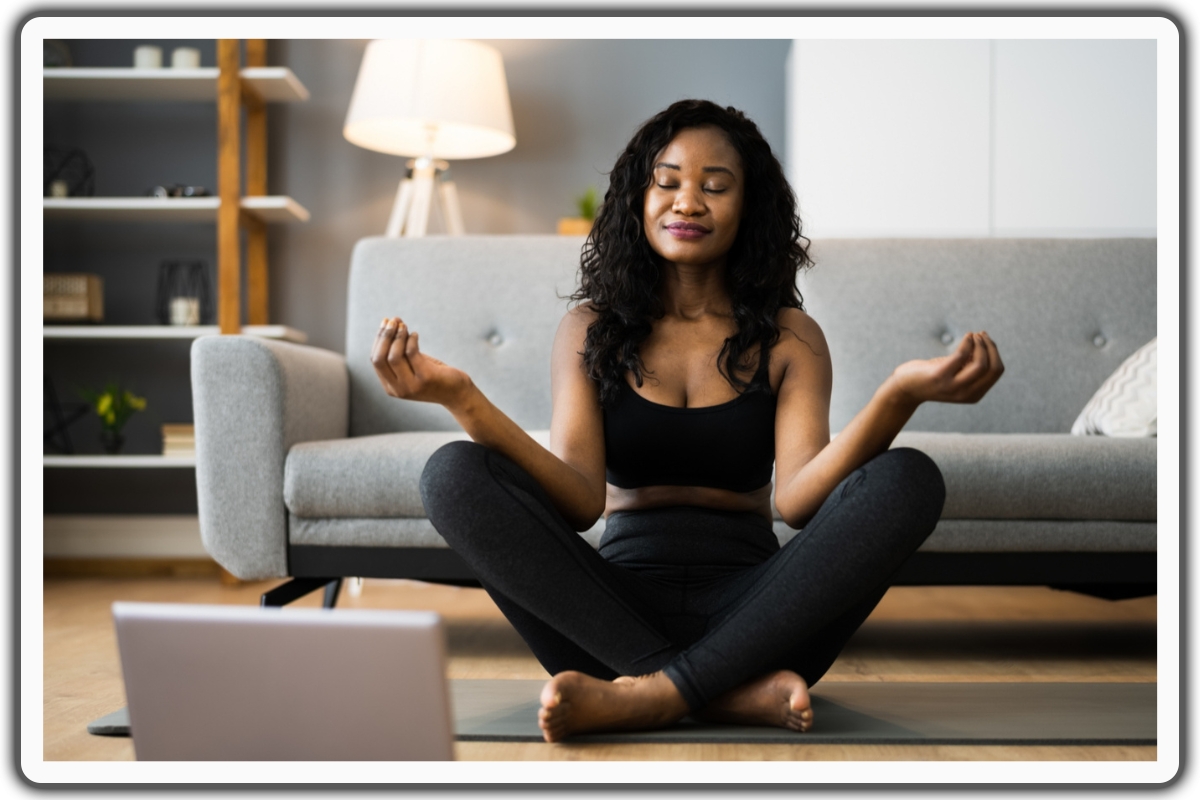

Stress management is vital for flu prevention.
Chronic stress weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses.
To maintain personal wellness and reduce the risk of flu infection, implementing stress reduction techniques is essential.
Meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga practices can effectively relieve stress and promote relaxation.
By proactively managing stress, people can strengthen their immune system, reduce the likelihood of flu infection, and support overall health and well-being.
Environmental Awareness
Environmental awareness is important for flu prevention, and having it can help deal with it.
It involves recognition of factors contributing to flu transmission, such as crowded spaces, close contact with sick individuals, and contaminated surfaces.
To minimize exposure to flu viruses in personal environments, individuals can take preventive measures.
This includes staying home when sick, and covering mouths and noses when coughing and sneezing. Wearing face masks in crowded settings can create a safer environment.
By being proactive and taking personal responsibility for flu prevention, individuals can help reduce the spread of the virus and protect both themselves and others.
Conclusion
Now that we've discussed what the flu virus is and the ways to prevent it, it is our responsibility to prevent it from spreading.
It all depends on how you do it; staying informed, taking preventive measures, being healthier, and vaccinating all contribute to the well-being of everyone around you.
So, as flu season comes and goes, don't forget your part to play.
Together, through our concerted efforts, we can stop the spread of the flu and build a healthier future for everyone.
References
American National Red Cross (2020). Flu (Influenza) Checklist.
https://www.redcross.org/content/dam/redcross/atg/PDF_s/Preparedness___Disaster_Recovery/Disaster_Preparedness/Flu/SeasonalFluChecklist.pdf
Greenbaum, E., Meinert E. (2009). Vaccinating Against the Flu: A Business Case. National Business Group on Health.
https://www.sfcdcp.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/Vaccinating-against-Flu-A-business-case-id795.pdf
Allen, E. (2024). Herd Immunity: How Vaccines Protect Your Community. University Health
https://www.universityhealth.com/blog/herd-immunity
